Why Shingles Vaccination is Important?

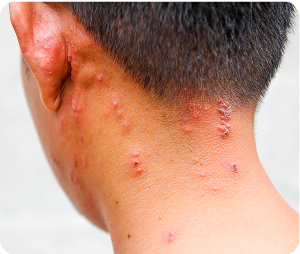
Shingles is caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus in people who previously have had chicken pox.1,2
1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.3
SHINGRIX (zoster vaccine recombinant, adjuvanted) for shingles



SHINGRIX vaccine given as a 2-dose series, with second shot administered 2 to 6 months after first shot.4
For immunodeficient or immunosuppressed individuals, SHINGRIX vaccine are given in shorter vaccination schedule; first dose at month 0 and second dose within 1 to 2 months later.4
Who needs SHINGRIX?

- CDC recommends SHINGRIX to prevent shingles and its complication in adults above 50 years.2
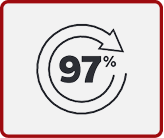
- SHINGRIX has 97% proven efficacy in adults ≥50 years and 91% in adults ≥70 years.1,5

- SHINGRIX for adults above 18 years who are at increased risk of shingles (immunocompromised individuals)4
CDC: Centre for Disease Control and Prevention; HZO: herpes zoster ophthalmicus; PHN: postherpetic neuralgia
Shingrix Safety Information4
Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any component of the vaccine. Very common adverse events include headache, gastrointestinal symptoms (including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and/or abdominal pain), myalgia, injection site reactions (such as pain, redness, swelling), fatigue, chills, fever.
References:
- Lal H, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015 May 28;372(22):2087-96
- CDC. Shingles [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/shingles/about/index.html. Accessed September 2024.
- Bollaerts K, et al. Epidemiol Infect. 2017; 145(13):2666-2677
- Shingrix Prescribing Information
- Cunningham AL, et al. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(11):1019-32.
- Strezova A, et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022;23:9(10)
- CDC. Shingles [Internet]. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/shingles/about/index.html. Accessed September 2024
For Malaysia Healthcare Professionals Only

Stay Connected


Shingrix Prescribing Information
Before prescribing, please refer to the full prescribing information, which is available via scanning this QR code. For any issues accessing the prescribing information via QR code, please contact GSK Malaysia at medinfo.my@gsk.com.
Home
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceutical Sdn Bhd
195801000141(3277-U)
HZ.01, Horizon Penthouse, 1 Powerhouse, 1,
Persiaran Bandar Utama, Bandar Utama,
47800 Petaling Jaya, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
Tel: (603) 2037 9808
www.my.gsk.com
PM-MY-BOO-WCNT-240004 05/25


